In this blog, we will cover the Introduction of Kubernetes and its Components.
What is Kubernetes
Kubernetes is an open source container management tool. You can set up a Kubernetes cluster on a Linux-based OS to deploy, manage, and scale Docker container applications on multiple hosts.
Kubernetes is made up of the following components:
- master
- nodes
- etcd
- network
These components are connected via a network, as shown in the following diagram:
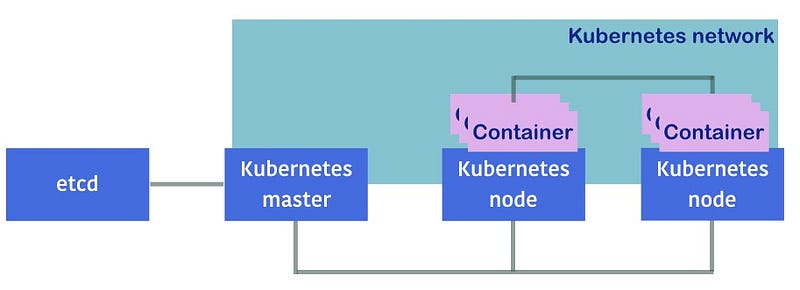
- Kubernetes master: It connects to etcd via HTTP or HTTPS to store the data
- Kubernetes nodes: It connect to the Kubernetes master via HTTP or HTTPS to get a command and report the status
- Kubernetes network: It L2, L3 or overlay make a connection of their container applications
Kubernetes master
The Kubernetes master is the main component of the Kubernetes cluster. It serves several functionalities, such as the following:
- Authorization and authentication
- RESTful API entry point
- Container deployment scheduler to Kubernetes nodes
- Scaling and replicating controllers
- Reading the configuration to set up a cluster
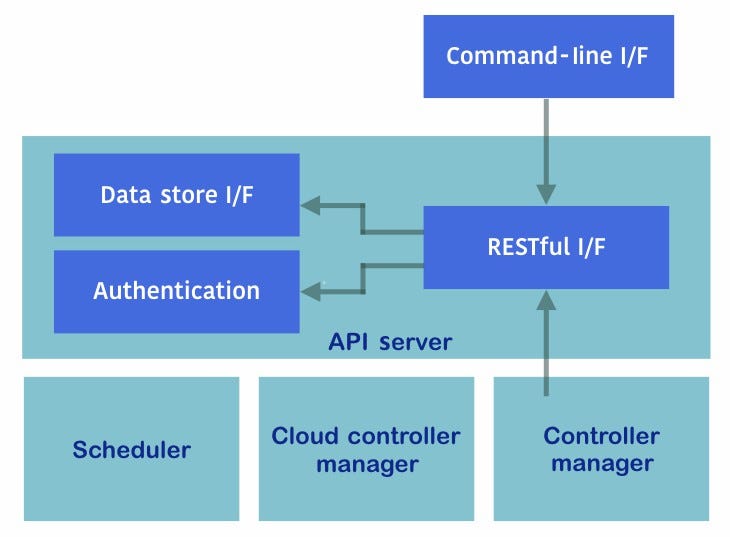
API server (kube-apiserver)
The API server provides an HTTP- or HTTPS-based RESTful API, which is the hub between Kubernetes components, such as kubectl, the scheduler, the replication controller, the etcd data store, the kubelet and kube-proxy, which runs on Kubernetes nodes, and so on.
Scheduler (kube-scheduler)
The scheduler helps to choose which container runs on which nodes. It is a simple algorithm that defines the priority for dispatching and binding containers to nodes. For example:
- CPU
- Memory
- How many containers are running?
Controller manager (kube-controller-manager)
The controller manager performs cluster operations. For example:
- Manages Kubernetes nodes
- Creates and updates the Kubernetes internal information
- Attempts to change the current status to the desired status
Command-line interface (kubectl)
After you install the Kubernetes master, you can use the Kubernetes command-line interface, kubectl, to control the Kubernetes cluster.
//see the nodes # kubectl get nodes NAME LABELS STATUS AGE kub-node1 kubernetes.io/hostname=kub-node1 Ready 26d kub-node2 kubernetes.io/hostname=kub-node2 Ready 26d
Kubernetes node
The Kubernetes node is a slave node in the Kubernetes cluster. It is controlled by the Kubernetes master to run container applications using Docker.
The following diagram displays the role and tasks of daemon processes in the node:
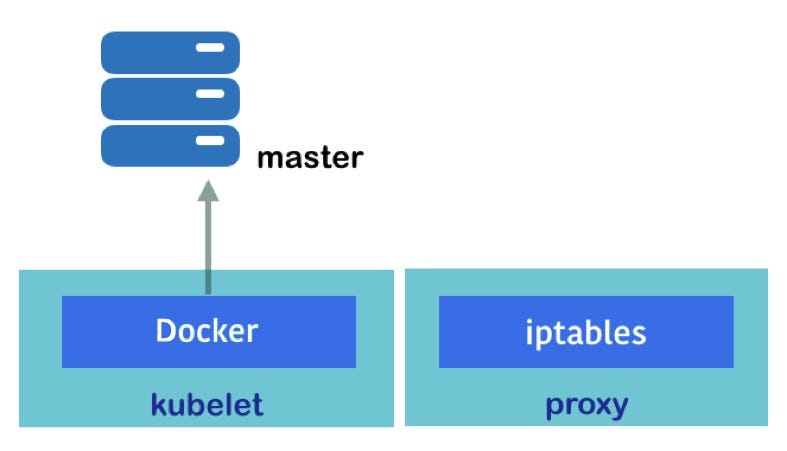
The node also has two daemon processes, named kubelet and kube-proxy, to support its functionalities.
kubelet
kubelet is the main process on the Kubernetes node that communicates with the Kubernetes master to handle the following operations:
- Periodically accesses the API controller to check and report
- Performs container operations
- Runs the HTTP server to provide simple APIs
Proxy (kube-proxy)
The proxy handles the network proxy and load balancer for each container. It changes Linux iptables rules (nat table) to control TCP and UDP packets across the containers.
etcd
etcd is the distributed key-value data store. It can be accessed via the RESTful API to perform CRUD operations over the network. Kubernetes uses etcd as the main data store.
Kubernetes network
Network communication between containers is the most difficult part. Because Kubernetes manages multiple nodes (hosts) running several containers, those containers on different nodes may need to communicate with each other.
If the container’s network communication is only within a single node, you can use Docker network or Docker compose to discover the peer. However, along with multiple nodes, Kubernetes uses an overlay network or container network interface (CNI) to achieve multiple container communication.
Congratulations !! We have successfully cover the Introduction of Kubernetes and its Components.