In this blog, we will explore how we can use the the configuration data like database details using Config Maps and Secrets.
Application ( Container Image) -> Deploy it on the Dev -> INT -> Prod
There is no change from the application, application remains the same in all the environments. The only thing which will change is the database details. So we need to make our application code in such a way that we can provide the environment specific data separately.
Kubernetes provides to associate environment-specific data with our application containers without changing our container image.
Config Map
- Used to define application-related data
- It decouples the application data from the application so that the same application can be ported across different environments.
- provides a way to inject customized data into running services from the same container image.
- used for non-sensitive configuration
kubectl create configmap --help
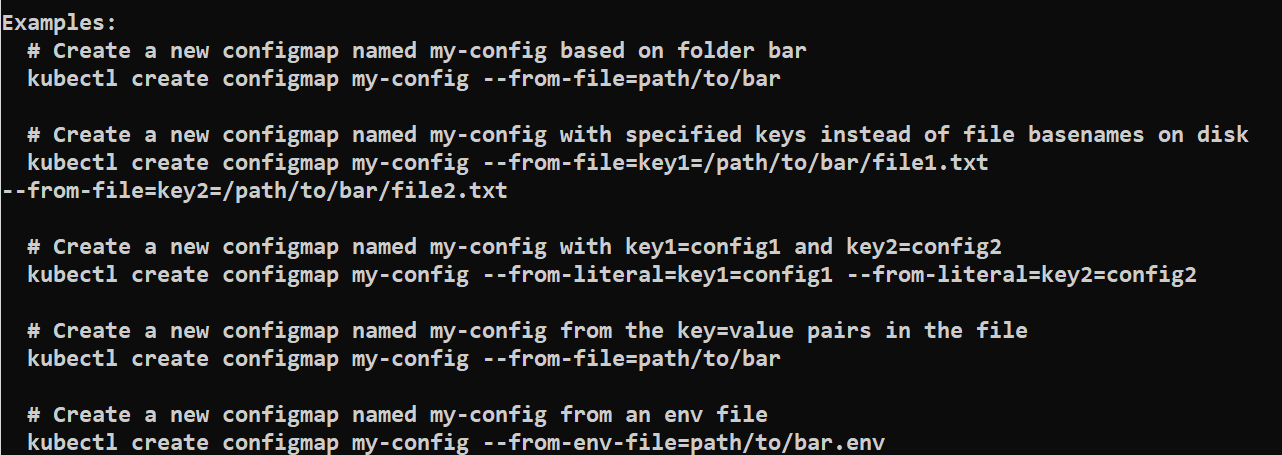
Command to create configmap
kubectl create configmap <map-name> <data-source>
Creating a ConfigMap from Literal Values
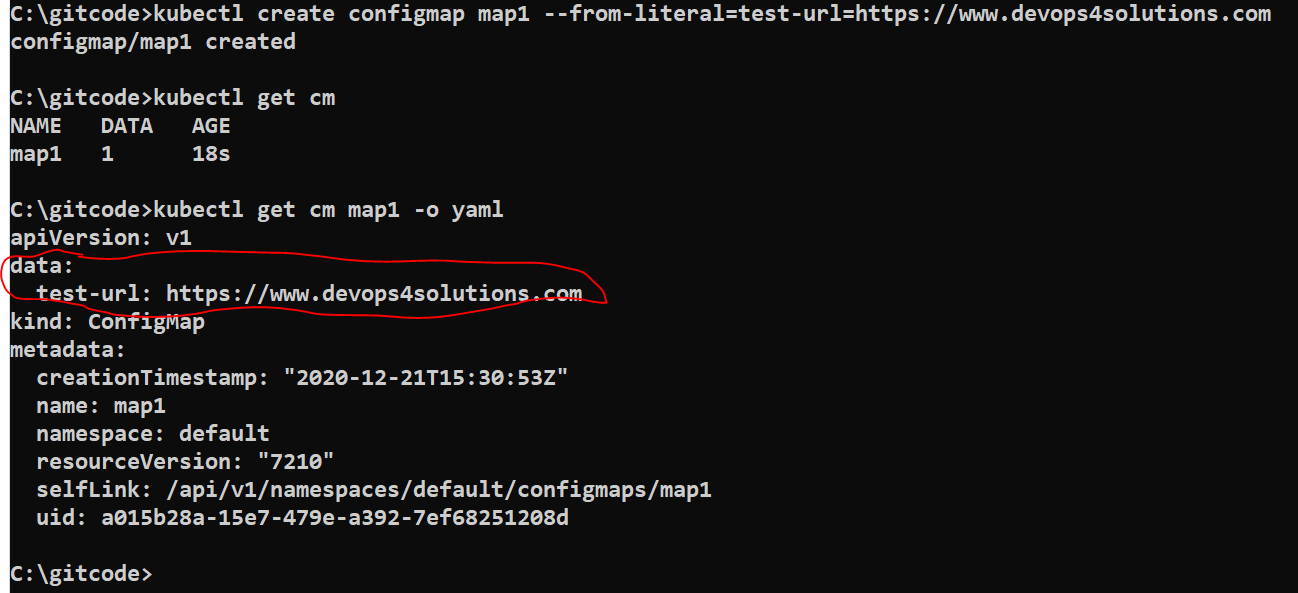
kubectl create configmap map1 --from-literal=test-url=https://www.devops4solutions.com kubectl get cm kubectl get cm map1 -o yaml
Now we will create a POD and inject this field
kind: Pod
apiVersion: v1
metadata:
name: pod-config-map
spec:
containers:
- name: container-1
image: busybox
command: ["/bin/sh","-c","env"]
envFrom:
- configMapRef:
name: map1
Create a POD
kubectl create -f pod-configMap.yaml
kubectl logs -f pod-config-map
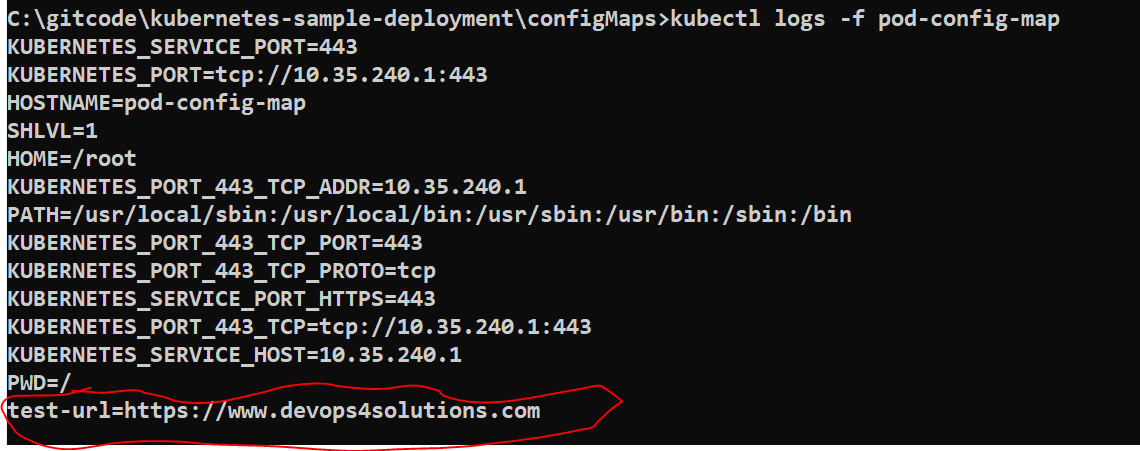
Now if we want to change the name
kind: Pod
apiVersion: v1
metadata:
name: pod-config-map-2
spec:
containers:
- name: container-1
image: busybox
command: ["/bin/sh","-c","env"]
env:
- name: new-name
valueFrom:
configMapKeyRef:
name: map1
key: test-url
Run the below command
kubectl create -f pod-configMap-2.yaml
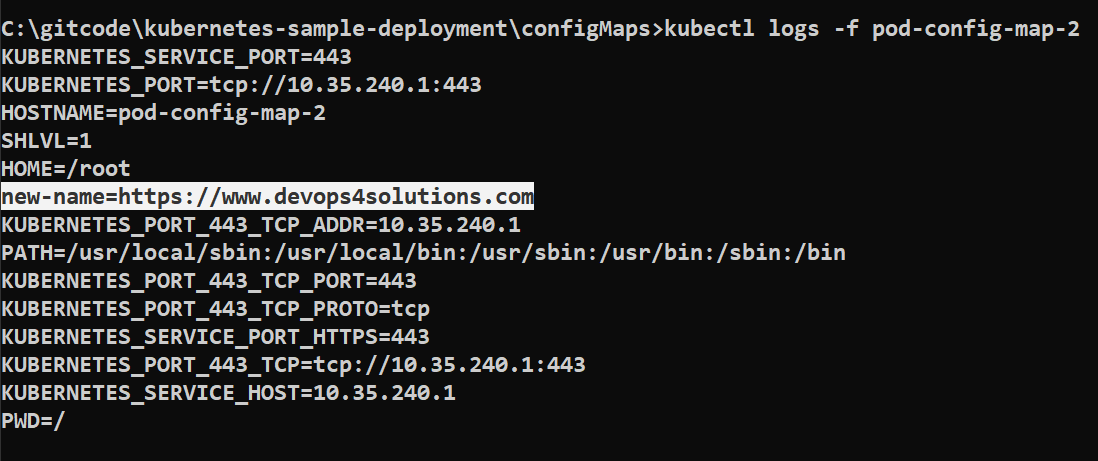
kubectl logs -f pod-config-map-2
Defining a ConfigMap from a File and Loading It onto a Pod
Let’s create a file application.properties with the below content
database_port=3743
database_user=admin
Create a configMap
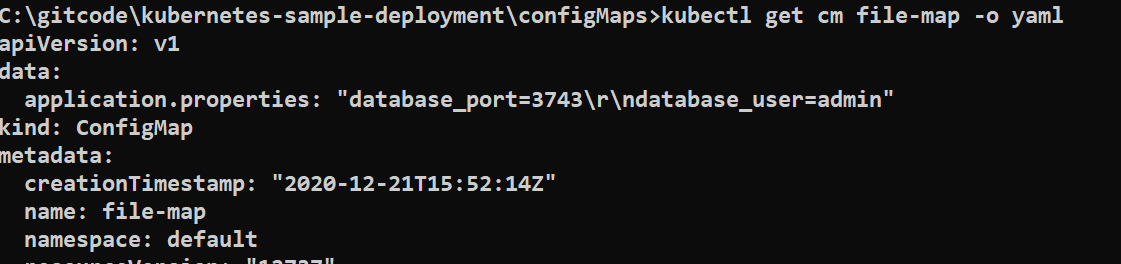
kubectl create configmap file-map --from-file=application.properties
kubectl get cm
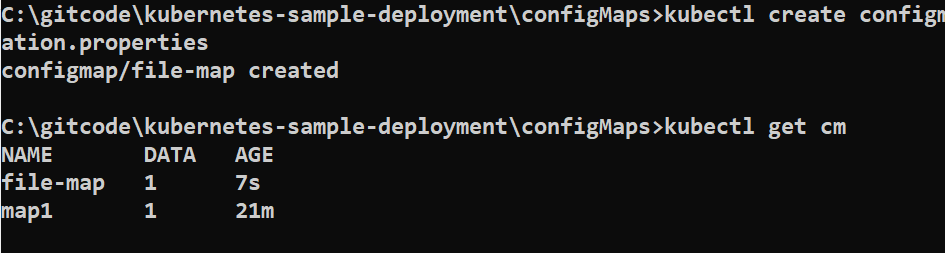
You can see both configMaps are showing Data as 1 but in our file we have defined two keys
Note that the name of the file, application.properties, becomes the key under the data section, and the entire file payload is the value of the key.
Now we will mount this config in a pod using volumes
kind: Pod
apiVersion: v1
metadata:
name: config-map-mount
spec:
containers:
- name: container-1
image: busybox
command: ["/bin/sh","-c","ls /etc/config/"]
volumeMounts:
- name: config-volume
mountPath: /etc/config
volumes:
- name: config-volume
configMap:
name: file-map
restartPolicy: Never
volumeMounts: Kubernetes mount the volume in /etc/config folder inside a container
volumes: defining the volume and providing the configMap name.
NOTE:
The name field under the volume and volumeMounts sections has to be the same so that Kubernetes can identify which volume is associated with which volumeMounts.
Run
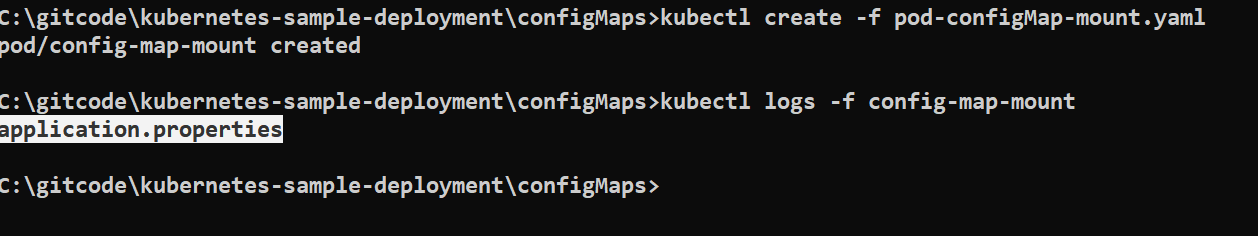
kubectl create -f pod-configMap-mount.yaml
kubectl logs -f config-map-mount
Secrets
Secrets are used to store the sensitive information like database passwords
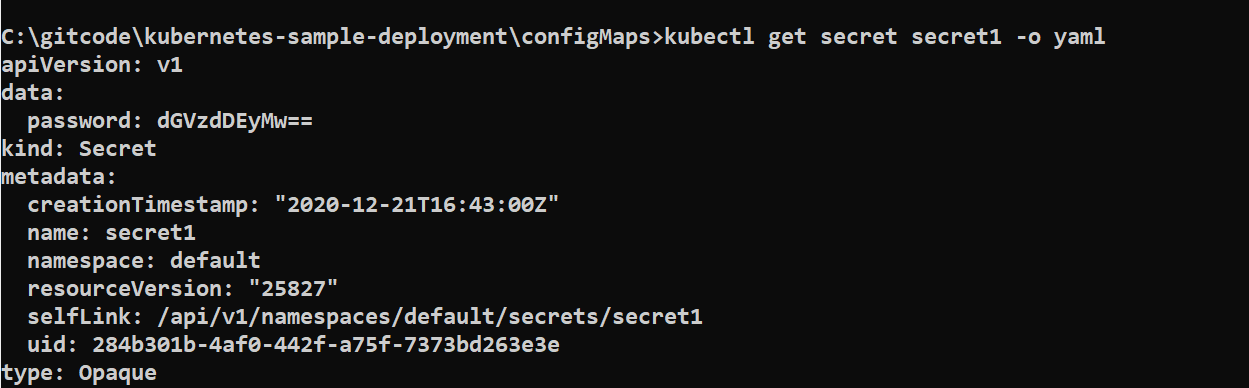
kubectl create secret generic secret1 --from-literal=password=test123
kubectl get secret secret1 -o yaml
Now to use this secret you can define in your yaml configuration as shown below:
envFrom:
- secretRef:
name: secret1