In this blog, we will Setting Up GitLab Runner on Windows to run the builds on the same system or on the another systems. Gitlab Runner concept is just like a agent/slave configuration that we use in Jenkins/Bamboo.
Introduction
GitLab Runner is used to create a pipeline/job to trigger the builds.
Types of Runners
- Shared
- Specific
- Group Runner
Shared Runners are useful for jobs that have similar requirements,
between multiple projects. Rather than having multiple Runners idling for
many projects, you can have a single or a small number of Runners that handle multiple projects. This makes it easier to maintain and update them.
Shared Runners process jobs using a fair usage queue.
In contrast to specific Runners that use a FIFO queue, this prevents
cases where projects create hundreds of jobs which can lead to eating all
available shared Runners resources. A Runner that serves all projects is called a shared Runner.
Specific Runners are useful for jobs that have special requirements or for
projects with a specific demand. If a job has certain requirements, you can set
up the specific Runner with this in mind, while not having to do this for all
Runners. For example, if you want to deploy a certain project, you can setup
a specific Runner to have the right credentials for this. The usage of tags
may be useful in this case. Specific Runners process jobs using a FIFO queue.
Group Runners are useful when you have multiple projects under one group
and would like all projects to have access to a set of Runners. Group Runners
process jobs using a FIFO queue.
Ideally, the GitLab Runner should not be installed on the same machine as GitLab.
Install GitLab Runner on Windows
For other Operating system , please refer this link
Prerequisite:
- Git installed
- A password for your user account, if you want to run it under your user account rather than the Built-in System Account
Installation Steps
- Create a folder , ex.:
C:\GitLab-Runner. - Download the binary for x86 or amd64 and put it into the folder you created. Rename the binary to
gitlab-runner.exe.
Registering a shared Runner
You can only register a shared Runner if you are an admin of the GitLab instance.
- Grab the shared-Runner token on the youtgitlaburl/
admin/runnerspage as shown below:
Note down the url and token

Shared Runners are enabled by default as of GitLab 8.2, but can be disabled with the Disable shared Runners button which is present under each project’s Settings ➔ CI/CD page
To register a Runner under Windows:
- Run the following command:
cd gitlab-runner gitlab-runner register
2. Enter your GitLab instance URL:
Please enter the gitlab-ci coordinator URL (e.g. https://gitlab.com )https://gitlab.com
3. Enter the token you obtained to register the Runner:
Please enter the gitlab-ci token for this runner xxx
4. Enter a description for the Runner, you can change this later in GitLab’s UI:
Please enter the gitlab-ci description for this runner [hostame] my-runner
5. Enter the tags associated with the Runner, you can change this later in GitLab’s UI:
Please enter the gitlab-ci tags for this runner (comma separated): my-tag,another-tag
6. Enter the Runner executor:
Please enter the executor: ssh, docker+machine, docker-ssh+machine, kubernetes, docker, parallels, virtualbox, docker-ssh, shell: docker
I have put shell

Run service using user account
You have to enter a valid password for the current user account, because it’s required to start the service by Windows:
gitlab-runner install --user ENTER-YOUR-USERNAME --password ENTER-YOUR-PASSWORD
gitlab-runner startIf you encounter an error like The account name is invalid try to add .\ before the username:
gitlab-runner install --user ".\ENTER-YOUR-USERNAME" --password "ENTER-YOUR-PASSWORD"Test the Setup
- Go to your specific project -> Click on the last symbol ->CI/CD Setting -> you will get the below screen

2. Expand Runners — you should see 1 runner under Shared Runner as green
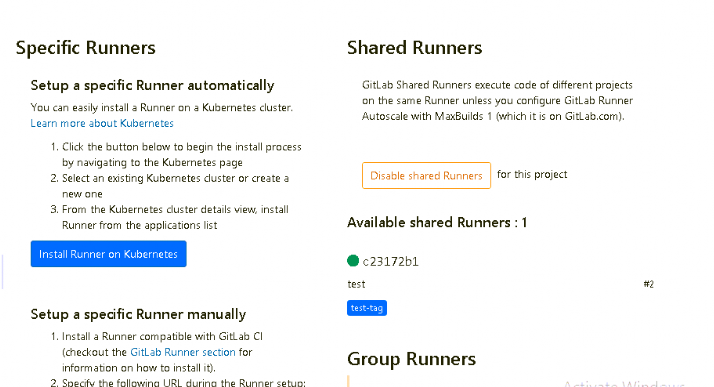
Setup is completed successfully. Now we will create a pipeline job.
How to Run GitLab Runner
- You have to create a .gitlab-ci.yml file at the root of your project. Sample yaml file as shown below:
pages: stage: deploy tags: — test-tag script: # run PowerShell Command — powershell -Command “Get-Date” # run PowerShell script — powershell -File copyFiles.ps1
- To skip the build , use [ci skip] in commit message so that pipeline/job will not triggered after every commit.
- Trigger the pipeline
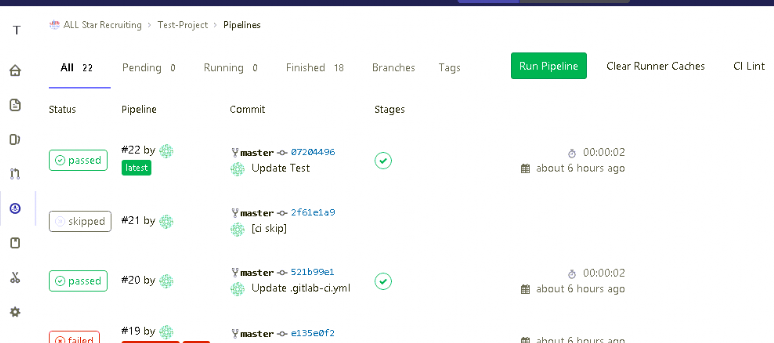
Finally congratulations!! You have successfully followed each and every step for Setting Up GitLab Runner on Windows.